2025 X-Ray Room Price Guide
For X-Ray Room pricing, you can expect to pay anywhere from $45,000 for entry-level machines and upwards of $200,000 for premium models. These are the average cost ranges for X-ray rooms in 2025 and price ranges include delivery, installation, and first-year service.
Entry-Level
Affordable Excellence
$45K-$59K
Entry-Level Units
AmRad FCFW Classic
Del systems
Quantum floor-mounted systems
Intermediate
Optimized Precision
$65K-$89K
Intermediate Level Units
AmRad DFMT Elite
GE Proteus
Siemens Ysio
GE Definium 5000
Premium
Luxury in Imaging Technology
$90K-$190K
Premium-Level Units
GE 646/656 Series
Siemens Ysio Max
Amrad OTS Intellect
Which X-ray Room
Price Tier is Right for You?
Now that you know some of the general features and capabilities, how do you go about choosing the best X-ray room?
Choosing the best rad room for your facility ultimately depends on your individual needs; What's your specialty? Do you have any budgetary restrictions? What's your average patient volume level?
This short video covers current price tiers to help you through the process of selecting your next X-ray room. Below are the typical features of each price tier.
Entry-Level
- Ideal for urgent cares and single-doctor practices
- Workflow: 7-10 patients a day
Intermediate
- Ideal for imaging centers or smaller orthopedic centers
- Workflow: 15-25 patients a day
- Features a fully functional table, elevating floating table
- No digital integration
Premium
- Ideal for a small to large hospital
- Workflow: 30+ patients a day
- Features an automated one-button touch to consistent movement
- Fully digitally integrated
What does an X-ray room consist of?
An x-ray room structurally consists of an exam room, control room, lead-lined door, lead-lined walls, and lead-lined glass window. It comes in different sizes, ranging from 10'x10', 12'x16', and larger.
Rad room configuration and equipment will heavily depend on the type of X-ray equipment your facility has. Features may include an on-light, generator, positioners, workstation, detector charger, lead vests, lead skirts, and apron racks.
Please note that each state has unique laws surrounding lead shielding.
To help, you can download the list we've compiled of Radiological and Health Department Links by State to direct your search.
How Many Types of
X-ray Machines Are There?
Learn the different types of X-ray machines from Rad Rooms to Portable X-Ray
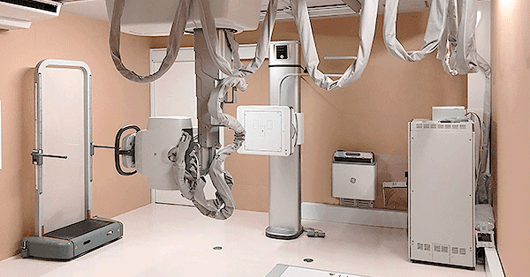
Digital X-Ray
Digital X-ray has revolutionized the way healthcare professionals obtain and analyze radiographic information.
Most importantly, digital sensors capture images electronically. Unlike traditional X-rays that require film processing, digital radiography streamlines the imaging process by providing instant access to high-quality images.
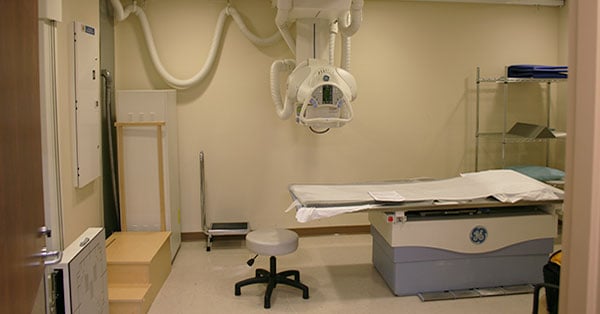
Analog X-Ray
Analog uses a more traditional processing technique. This method exposes the body to X-ray beams, which create an image on a photographic film. The film is then developed in a darkroom using specific chemicals, much like the process used for traditional camera films. Because of this lengthy process, analog X-ray development takes much longer than digital.

Portable X-Ray
A portable or mobile X-ray is a versatile, non-fixed unit designed to move effortlessly within a facility. Healthcare professionals can enhance their patient workflow by bringing the equipment directly to their patients' locations.
Because they use lower radiation dosage, portable X-rays do not require lead-lined rooms for scanning. This reduces radiation exposure and allows for easy transportation and flexibility in a variety of medical settings.
Digital Radiography vs. Computed Radiography
The choice between digital radiography (DR) and computed radiography (CR) holds considerable significance. Both technologies represent pivotal advancements from traditional film-based methods, introducing efficiency and enhanced imaging capabilities.

DR
Digital radiography (DR) uses flat panel detectors to produce a digital image. Unlike traditional X-ray methods that require film development in a darkroom, digital radiography provides instant access to clear and detailed digital X-ray images.
Even though DR systems come with a higher initial investment, they often result in lower long-term expenses due to their minimal maintenance requirements.
- High-resolution image quality
- Fully digitized configuration
- Swift image viewing (within 1 minute)
- Limited portability unless utilizing newer wireless systems
- Reduced risk of overexposure to radiation
The International Atomic Energy Agency breaks down the features and benefits of digital radiology and how these advancements are improving medical services.
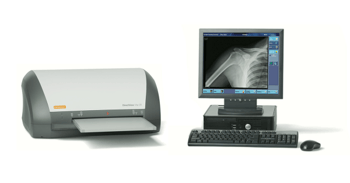
CR
Computed Radiography or CR is replacing traditional film radiography. CR systems use cassette-based phosphor storage plates (PSP) to capture images. These systems tend to be more cost-effective as they have a lower initial investment then digital radiography. While you gain flexibility, your image quality will not be as high-resolution. Overall, here are a few features to keep in mind with a CR based system.
- Lower-resolution images
- More labor-intensive due to plate storage and transfer
- Bulky design
- Increased portability and flexibility
- Increased risk of radiation over-exposure
- Prone to damage and requires more maintenance
For a more detailed explanation of computed radiography, click here to learn more!
More X-ray Resources
Visit the Block Imaging learning center for more Xray-related blogs, videos, and guides.
FREE DIGITAL X-RAY CONVERSION GUIDE
Explore the possibilities for transitioning your analog X-ray system to a digital format. Use this step-by-step guide to learn how your analog X-ray equipment can produce crisp, convenient digital images.
You'll discover:
• Three methods for going digital
• Pros and cons of each method
• Average costs for each method
Click the button below to become an X-ray expert - no contact information is required!

4 min read
Why Hospitals Keep Choosing R/F Rooms (Despite the Upfront Investment)
Clay Selby: Jun 27, 2024
3 min read
Comparing GE Optima 220 & 240 Portable X-ray Machines
Clay Selby: Jun 10, 2024



