Updated: April 22, 2025 : 3 min read
DARC1 vs. DARC2 vs. VDARC: CT Scanner Part Systems and Troubleshooting
Is your CT scanner’s performance dependent on a system you might not even know about?
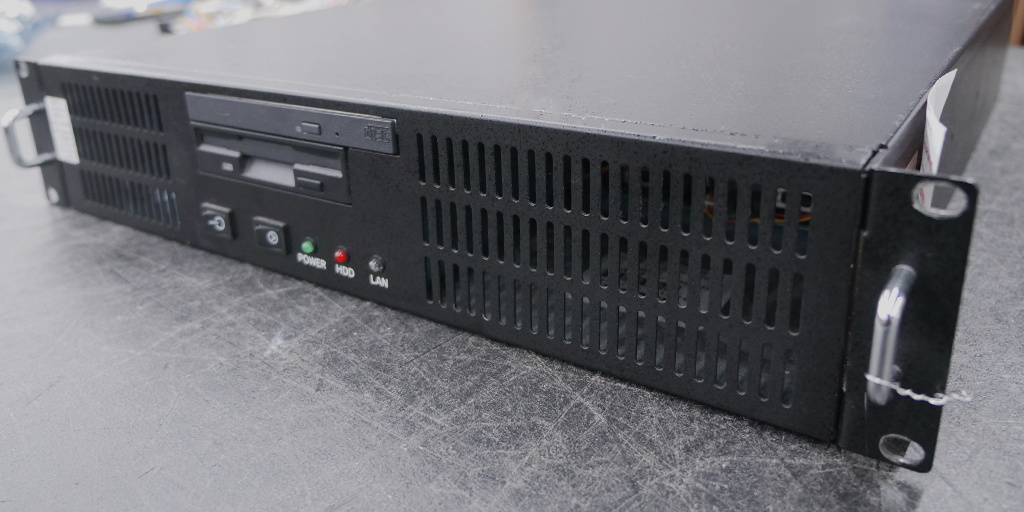
The technology that powers image processing and data acquisition in many older CT machines comes from a critical component: the DARC system.
Without this system, these CT scanners would struggle to deliver the high-quality images required for diagnostics. In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of DARC systems—DARC1, DARC2, and VDARC—and help you identify and troubleshoot any issues that may occur with your CT system.
Need to replace your Darc or another part?
Visit our parts inventory to find the exact components you need or reach out to our team for guidance on selecting the right replacement for your system.
Let us help you avoid disruptions and maintain peak performance!
DARC1 (GOC3 Console): Supporting Legacy CT Systems
DARC1 is the data processing system for older CT machines, primarily those manufactured in the early 2000s.
If you’re working with a legacy system, such as the GE Lightspeed CT (4- to 16-slice) from the late 1990s to early 2000s, your machine likely relies on DARC1. These systems handle data acquisition through external arrays. This means image generation happens outside of the DARC unit.
Though this external processing setup may seem outdated by today’s standards, many facilities still use DARC1 for its reliability and flexibility, particularly in handling 4- to 16-slice DIP cards.
DARC2 (GOC4 Console): Enhancing Mid-Tier Systems
As CT technology advanced, faster data processing was necessary. And this led to the development of DARC2.
This system, found in CT machines manufactured in the mid-2000s, integrates internal scan drives that improve the speed of data acquisition and processing. CT systems like the GE Lightspeed VCT (released in 2004), the Siemens Sensation 64 (introduced in 2005), and the Philips Brilliance 64 (also from 2005) typically use a DARC2.
For facilities using 64-slice systems, DARC2 brings faster performance and improved reliability.
It has some features in common with DARC1, such as the use of interchangeable DIP cards, but with internal scan drives, it offers quicker turnaround times for imaging tasks.
VDARC (GOC5 Console): Powering Advanced Systems
The most advanced DARC system, VDARC, supports more modern CT machines built in the mid-2010s and beyond. These include the GE Revolution CT (released in 2014), the Toshiba Aquilion ONE (introduced in 2007 and updated in later models like the 2015 GENESIS edition), and the Siemens Force (released in 2014).
VDARC is designed to handle high-speed data acquisition and large imaging volumes which are essential for multi-slice and ultra-fast scanners.
With more sophisticated scan drive configurations than its predecessors, VDARC is built to support the heavy data loads of modern imaging systems while maintaining flexibility through interchangeable DIP cards.
Understanding the DIP Card
A key component of every DARC system is the Digital Interface Processor (DIP) card.
The DIP card is a fiber optic board responsible for transmitting all image data from the gantry to the DARC system. And they contain vital system data that is transferable between DARC units. That data is particularly important when replacing or upgrading a DARC system.
Most replacement DARCs are sold without a DIP card, meaning that the DIP card from your existing unit must be re-used to ensure smooth integration and continued functionality.
What is the Lifespan of a DARC?
The typical lifespan of a DARC unit is around 3 to 5 years, after which performance issues may begin to arise.
Software Failing to Boot Up? Diagnose and Fix Your DARC
One of the most common signs of DARC failure is software that fails to boot properly.
When this happens, your imaging processes could come to a complete halt and will require immediate attention to avoid extended downtime.
To help mitigate this, here are a few key troubleshooting tips that can help technicians and engineers quickly assess and resolve the issue:
- Check the Hard Drive: Before deciding to replace the entire DARC system, consider replacing the hard drive first. Software boot-up issues are often caused by hard drive failures, and this solution could be a cost-effective way to restore functionality.
- Inspect the DIP Card: It’s important to ensure that the card is securely installed and free of physical damage. A malfunctioning or improperly connected DIP card could interrupt the entire data acquisition process.
- Consult System Documentation: Every CT system will come with detailed troubleshooting guides that list specific error codes and symptoms. These resources can be invaluable for diagnosing issues more precisely before deciding on the next steps.
If none of these steps resolve the problem, it might be time to consider replacing the entire DARC unit. When doing so, remember to transfer the DIP card from your current DARC to the new system.
Where Can I Find My DARC Model Number?
Each DARC system has unique features and requires specific upgrades, maintenance, and troubleshooting depending on the manufacturer and model number.
Your model number should be located on the side panel of the DARC system.

Keeping Your Imaging System Running Smoothly
By identifying potential problems early and learning basic troubleshooting steps, you can help keep your imaging operations running smoothly.
If you need further assistance or have questions about maintaining or troubleshooting your DARC system, don’t hesitate to contact our team of experts. We’re here to help you keep your imaging systems running smoothly.

Sheldon Schehr